Girls’ body parts | Different 50 body parts name female with pictures. Learn these body parts’ names in English to increase your vocabulary power. As an English-speaking country, it’s important to learn everyone about girls’ body parts names. Learning the names of body parts can be a fun and useful exercise for communication and travel.
50 Body Parts Name Female
Let’s learn women body parts name with pictures:
| No. | Image | Body Part Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | Head |
| 2 |  | Hair |
| 3 |  | Eyes |
| 4 |  | Nose |
| 5 |  | Ears |
| 6 |  | Mouth |
| 7 |  | Lips |
| 8 |  | Teeth |
| 9 |  | Tongue |
| 10 |  | Throat |
| 11 |  | Neck |
| 12 |  | Shoulders |
| 13 |  | Armpit |
| 14 |  | Elbows |
| 15 |  | Forearms |
| 16 |  | Hands |
| 17 |  | Fingers |
| 18 |  | Nails |
| 19 |  | Chest |
| 20 |  | Breasts |
| 21 |  | Ribcage |
| 22 |  | Abdomen |
| 23 |  | Stomach |
| 24 | 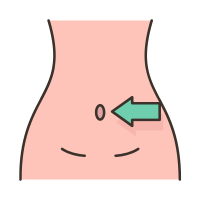 | Navel |
| 25 |  | Hips |
| 26 | 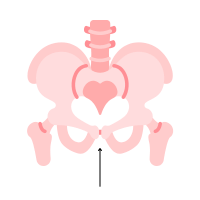 | Pelvis |
| 27 |  | Back |
| 28 |  | Spine |
| 29 |  | Buttocks |
| 30 |  | Eyebrow |
| 31 |  | Vagina |
| 32 | 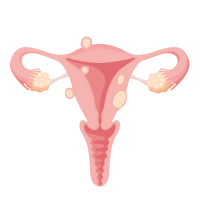 | Uterus |
| 33 |  | Ovaries |
| 34 |  | Fallopian Tubes |
| 35 |  | Clitoris |
| 36 |  | Labia |
| 37 |  | Anus |
| 38 |  | Legs |
| 39 |  | Thighs |
| 40 |  | Knees |
| 41 |  | Shins |
| 42 |  | Calves |
| 43 |  | Ankles |
| 44 |  | Feet |
| 45 |  | Toes |
| 46 |  | Soles |
| 47 |  | Heels |
| 48 |  | Arch of the Foot |
| 49 |  | Achilles Tendon |
| 50 |  | Collarbone (Clavicle) |
Female body parts name in Detail
1. Head

The upper part of the body containing the brain. Eyes that speak volumes, and lips that whisper secrets.
2. Hair

Strands growing from the scalp. A versatile and expressive canvas for women to showcase their style and personality.
Eyes

Organs for visual perception. The eye, a complex organ that allows us to see the world in all its beauty and wonder.
Nose

The protruding part above the mouth for smelling. The nose is a facial feature that protrudes from the center of the face and is used for breathing and smelling.
Ears

Organs for hearing and balance. Ears are sensory organs located on the sides of the head, responsible for hearing and maintaining balance.
Mouth

Opening for speaking, eating, and breathing. The mouth is the opening in the face where food is taken in, and where speech and sound are produced. It is also a key component of the digestive and respiratory systems.
Lips

Soft tissue surrounding the mouth. Lips are soft, fleshy folds at the entrance of the mouth, used for speaking, eating, and expressing emotions through movements.
Teeth

Hard structures for chewing food. Teeth are hard, calcified structures in the mouth used for biting, chewing, and grinding food.
Tongue

Muscular organ inside the mouth for taste. The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth used for tasting, swallowing, and speaking.
Throat

Passage for food and air, including the esophagus. The throat is the passage that connects the mouth and nose to the esophagus and trachea, allowing for swallowing and breathing.
Neck

Connects the head to the body. The neck is the part of the body that connects the head to the torso and is responsible for supporting the weight of the head and allowing for movement.
Shoulders

Upper part of the arms connecting to the torso. Shoulders are the uppermost part of the human arm and connect the arm to the torso. They provide support and mobility for the arms and are essential for various activities.
Armpit

Limbs from shoulders to wrists. The armpit is the hollow area beneath the junction of the upper arm and the shoulder, typically containing sweat glands and hair follicles.
Elbows
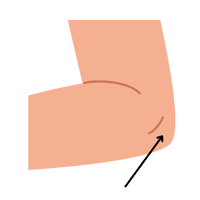
Joint between upper and lower arm. The joint connecting the upper and lower arms, allowing for bending and straightening movements.
Fingers

Digits at the end of the hands. Fingers are the five slender, jointed extensions at the end of the hand, used for gripping and manipulating objects.
Nails

Hard protective coverings on fingers. Nails are hard, protective coverings on the tips of fingers and toes. They are made of a protein called keratin and serve to protect the underlying tissue.
Chest

Upper part of the torso housing vital organs. The chest is the front part of the upper body, located between the neck and abdomen, housing vital organs such as the heart and lungs.
Breasts

Mammary glands on the chest. Breasts are mammary glands located on the chest of female mammals, primarily used for breastfeeding offspring and as secondary sexual characteristics in humans.
Ribcage

Bony structure protecting the heart and lungs. The ribcage is a bony structure in the chest that protects the heart and lungs.
Abdomen

Lower part of the torso containing organs. The abdomen is the lower part of the torso, containing the stomach, intestines, and other vital organs.
Stomach

Digestive organ between the chest and abdomen. The stomach is a muscular organ in the digestive system that stores and breaks down food.
Navel
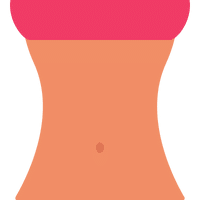
Small scar from the umbilical cord. The navel, also known as the belly button, is the small, scar-like indentation in the center of the abdomen where the umbilical cord was attached during fetal development.
Hips

Upper part of the pelvis. The hips are the joint where the upper thigh bone (femur) connects to the pelvis. They provide stability and support for the lower body and are involved in various movements such as walking and running.
Pelvis
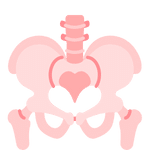
Bony structure connecting the spine and legs. The pelvis is the bony structure located at the base of the spine, consisting of the hip bones and sacrum. It provides support for the spine and houses the reproductive and digestive organs.
Back

Rear side of the torso, including the spine. The back is the posterior part of the human body, extending from the neck to the waist, and consisting of the spine, muscles, and skin.
Spine

Column of bones running down the back. The spine is the central column of bones in the back that provides support and protection for the spinal cord.
Buttocks

Muscles on the rear end of the pelvis. The buttocks are the rounded, fleshy area located at the back of the hips and below the waist, consisting of muscles and fat tissue.
50 Body Parts Name Female
Let’s see more than fifty body parts of woman name with picture:
- Head
- Hair
- Forehead
- Eyebrow
- Eyelash
- Eye
- Ear
- Nose
- Cheek
- Mouth
- Lip
- Tooth
- Tongue
- Chin
- Neck
- Shoulder
- Arm
- Elbow
- Wrist
- Hand
- Finger
- Thumb
- Chest
- Breast
- Rib
- Back
- Waist
- Hip
- Buttocks
- Leg
- Thigh
- Knee
- Calf
- Ankle
- Foot
- Toe
- Heel
- Sole
- Skin
- Navel
- Belly
- Palm
- Knuckle
- Joint
- Pelvis
- Shin
- Muscle
- Tendon
- Vein
- Heart
FAQs on Body parts name Female
Q1: What are the main parts of a female’s body?
A1: The main parts of a female’s body include the head, arms, chest, stomach, legs, and more. These are the basic parts that make up the human body.
Q2: What is the chest area called on a female?
A2: The chest area of a female is commonly referred to as the “breast” or “chest.”
Q3: What is the lower part of the body called in females?
A3: The lower part of the body in females is often called the “abdomen” or “belly.” This area is below the chest and above the legs.
Q4: What are the two parts of the female reproductive system?
A4: The two main parts of the female reproductive system are the “ovaries” and the “uterus.” Ovaries produce eggs, and the uterus is where a baby grows during pregnancy.
Q5: What is the name of the external part of the female reproductive system?
A5: The external part of the female reproductive system is called the “vulva.” It includes the opening of the vagina, the clitoris, and other surrounding parts.
Q6: What is the proper name for the female private parts?
A6: The proper name for the female private parts is the “vagina.” It is the muscular tube that connects the uterus to the external body.
Q7: What is the purpose of the breasts in females?
A7: The breasts in females have a dual purpose. They can provide milk to nourish a baby (breastfeeding) and are also a part of the body’s appearance.
Q8: What is the difference between a vulva and a vagina?
A8: The vulva is the external part of the female genitalia, including the opening, while the vagina is the internal muscular tube that connects to the uterus.
Q9: What is the name of the small organ above the opening of the vagina?
A9: The small organ above the opening of the vagina is called the “clitoris.” It is sensitive and plays a role in sexual pleasure.
Q10: What is the function of the uterus in females?
A10: The uterus is where a baby grows during pregnancy. It provides a safe space for the developing baby and contracts during labor to help with childbirth.
Related posts:
- Body Parts Name Female
- Woman Body Parts Name
- Nabhi Body Parts Name in English
- Body Parts Name
- Cat Anatomy
- All Skin Tones Names
- 100+ Cute Names For Feet