An ecosystem is a community of living things, like animals and plants, that interact with each other and their environment. It’s like a big family of nature where everyone plays a role to keep things balanced and healthy.

What is Ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a big community of living things like plants and animals. They all depend on each other and their environment to survive.
It’s like a team where everyone has a special role to play and they work together to keep everything in balance.
For example, plants give us oxygen to breathe, and animals help to spread seeds for new plants. So, all the parts of an ecosystem help each other stay alive and healthy!
Read more and explore the structure components and types of ecosystems and their functions
Structure of Ecosystem
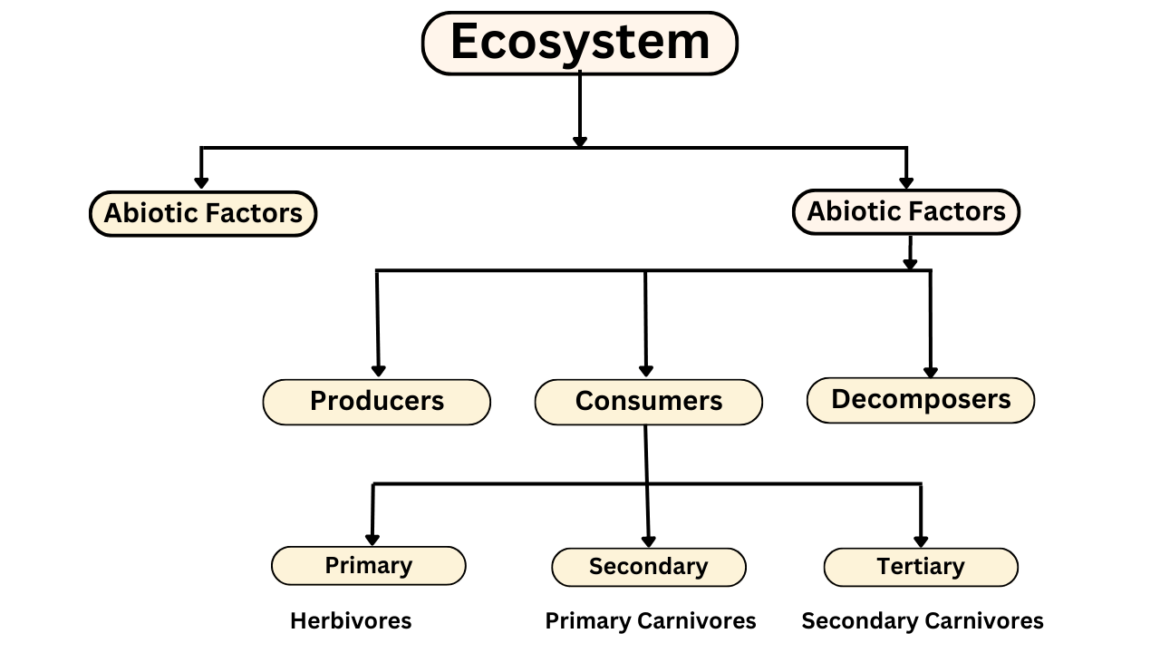
The structure of an ecosystem can be characterized in two ways, The first one is boutique, and the second one is abiotic components.
This is all about how energy is spread around us, like how sunlight warms the Earth or how wind moves the air. whether it’s hot, cold, rainy, or snowy. So, it’s about how things like heat, light, and weather are shared in the world around us.
The Structure of the ecosystem can be split into two ways:
- Biotic Components
- Abiotic Components
the Biotic components and Abiotic components are interrelated to the ecosystem It is an open system where energy and components can flow throughout the boundaries from the below chart You may have understood in a better way.
Biotic Components
Biotic components refer to all living things in an ecosystem. These are the living organisms that play a crucial role in the environment. Let’s explore some of the key biotic components:
Plants: Plants are living organisms that make their own food through a process called photosynthesis. They are essential because they provide food and oxygen for other living creatures, including animals and humans.
Animals: Animals are living beings that can move, eat food, and reproduce. They come in various shapes and sizes, from tiny insects to large mammals. They play an important role in the ecosystem by helping with pollination, seed dispersal, and even controlling populations of other organisms.
Humans: Yes, humans are part of the biotic components too! We are living beings that have a significant impact on the environment. We interact with other living things and influence the balance of the ecosystem through our actions.
Microorganisms: These are tiny living organisms that are not visible to the naked eye. Examples include bacteria and fungi. Microorganisms are essential for breaking down dead plants and animals, recycling nutrients, and maintaining soil health.
Fungi: Fungi are a type of living organism that can’t make their own food like plants do. Instead, they help break down dead plants and animals, releasing nutrients back into the soil. Some fungi also form partnerships with plants, helping them absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
Insects and Other Invertebrates: Insects, spiders, worms, and other invertebrates are important biotic components. They have various roles in an ecosystem, like pollinating plants, decomposing organic matter, and serving as food for other animals.
Birds: Birds are flying animals that play a vital role in seed dispersal and insect control. They can carry seeds to new places, helping plants spread, and they eat many insects, keeping their populations in check.
Fish and Aquatic Life: In aquatic ecosystems like oceans, rivers, and lakes, fish and other aquatic creatures are essential biotic components. They contribute to the food chain and help maintain the balance of underwater life.
Mammals: Mammals are warm-blooded animals that give birth to live young and nurse them with milk. They are part of various ecosystems and contribute to the diversity of life on Earth.
Abiotic Components
Abiotic components are the non-living parts of an ecosystem, which means they are not alive. These elements play a crucial role in shaping the environment and supporting life. Here are some important abiotic components:
Sunlight: Sunlight is the primary source of energy for all living things. It provides light and heat, which is essential for plants to make their food through a process called photosynthesis.
Air (Atmosphere): The air around us is made up of different gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide. Living organisms, especially animals, need oxygen from the air to breathe and survive.
Water: Water is vital for life. It is used by plants and animals for various purposes, such as drinking, bathing, and supporting plant growth. Without water, life cannot exist.
Soil: Soil is the layer of earth where plants grow their roots. It provides nutrients and support to plants. The soil is made up of small pieces of rock, minerals, organic matter (like dead plants and animals), and water.
Temperature: Temperature refers to how hot or cold the environment is. Different living things thrive in different temperature ranges, and extreme temperatures can affect their survival.
Climate: Climate is the long-term pattern of weather conditions in an area. It includes factors like temperature, humidity, and precipitation. Climate influences the types of plants and animals that can live in an ecosystem.
Wind: Wind is the movement of air. It helps in dispersing seeds and pollens, which aids in the reproduction of plants.
Rocks and Minerals: Rocks and minerals are part of the Earth’s crust. They contribute to the formation of the soil and also provide habitats for some organisms.
Natural Disasters: While not part of a typical ecosystem, natural disasters like earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and hurricanes can significantly impact the abiotic components of an area, leading to changes in the ecosystem.
Functions of Ecosystem
- Provide Habitat: Ecosystems give animals and plants a place to live and find food, water, and shelter.
- Clean Air and Water: They help to clean the air we breathe and the water we drink, making it healthier for us and other living things.
- Support Life: Ecosystems support a wide variety of living things, like animals, plants, and microorganisms.
- Cycle Nutrients: They recycle nutrients, such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus, which are essential for life.
- Pollination: Ecosystems help with pollination, where insects and birds move pollen between plants, helping them make fruits and seeds.
- Control Pests: They can control pests naturally by keeping the balance of different species in check.
- Flood and Erosion Control: Ecosystems can reduce the risk of floods and erosion by absorbing and slowing down water.
- Climate Regulation: They play a role in regulating the climate, helping to maintain a balance of temperature and weather patterns.
- Provide Food: Ecosystems offer us various types of food like fruits, vegetables, and meat that come from plants and animals.
- Recreation and Enjoyment: Ecosystems give us beautiful places to explore and enjoy nature.
Types of Ecosystems
There are two types of ecosystems i.e:
- Terrestrial Ecosystems
- Aquatic Ecosystem
Terrestrial Ecosystems
Terrestrial ecosystems are places on Earth where living things, like plants and animals, interact with each other and their environment. These areas include forests, grasslands, deserts, and more.
Terrestrial ecosystems are categorized into four groups.
- Forest Ecosystem
- Grassland Ecosystem
- Tundra Ecosystem
- Desert Ecosystem
Forest Ecosystem
A forest ecosystem is a place where many plants, animals, and tiny living things work together with the environment. Forests are important because they help keep the Earth’s temperature balanced and store a lot of carbon, which is good for the planet.
Grassland Ecosystem
Grassland ecosystems are places where grass and small plants are abundant. Examples include temperate grasslands and tropical savannas.
Temperate grasslands: Temperate grasslands are vast lands covered in short, tough grasses.
Tropical Savannas: Tropical savannas are hot, grassy areas with scattered trees where lions and elephants roam. It’s like a vast, sunny playground for wild animals.
Tundra Ecosystem
Tundra ecosystems are icy and treeless, found in cold places with little rain. They stay snowy most of the time. They’re seen in the Arctic and on mountaintops.
Desert Ecosystem
Deserts are places on Earth where it hardly ever rains, and there are very few plants. It’s super hot during the day and really cold at night.
Aquatic Ecosystem
An aquatic ecosystem is a community of living organisms (like plants and animals) and their environment (water) found in water bodies like oceans, seas, rivers, lakes, and ponds.
Types of Aquatic Ecosystems:
- Marine Ecosystem
- Freshwater Ecosystem
Marine Ecosystem
The marine ecosystem includes the vast oceans and seas. They have lots of salt and many different types of living things compared to freshwater areas.
Freshwater Ecosystem
The freshwater ecosystem is a watery place where there is no salt, like in lakes, rivers, and ponds. It’s where many animals and plants live and depend on clean water to survive.
FOOD CHAIN

FAQs Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is an ecosystem?
A1: An ecosystem is a place where living things, like plants and animals, live together and interact with each other and their environment.
Q2: What are living things in an ecosystem?
A2: Living things in an ecosystem are plants, animals, insects, and other creatures.
Q3: What are non-living things in an ecosystem?
A3: Non-living things in an ecosystem are things like sunlight, air, water, rocks, and soil.
Q4: How do plants and animals depend on each other in an ecosystem?
A4: Plants provide food and oxygen for animals, while animals help plants by pollinating them and spreading their seeds.
Q5: How do changes in an ecosystem affect plants and animals?
A5: Changes like pollution, deforestation, or climate change can harm plants and animals, making it hard for them to survive.
Q6: Why are bees important in an ecosystem?
A6: Bees are important because they help pollinate flowers, which allows plants to make fruits and seeds.
Q7: How can we protect an ecosystem?
A7: We can protect an ecosystem by not littering, using resources wisely, and taking care of plants and animals.
Q8: What happens if one animal disappears from an ecosystem?
A8: If one animal disappears, it can disrupt the food chain, affecting other animals and plants in the ecosystem.
Q9: Why is it important to keep a balance in an ecosystem?
A9: Keeping a balance in an ecosystem helps all living things survive and stay healthy.
Q10: Can you give examples of different ecosystems?
A10: Yes, some examples are a forest ecosystem, a desert ecosystem, and an ocean ecosystem. Each has unique plants and animals adapted to their environment.