English grammar is essential for every student and for English speakers. It enables effective communication. Grammar is a set of rules. It tells us how to build sentences, use words, and make sense when we talk and write. It’s like the instruction manual for clear and correct communication in English Language. Using proper grammar improves effective communication.
Grammar is the backbone of effective communication in English.
It provides the structure and rules that ensure words and sentences convey precise meanings.
Proper grammar enhances clarity, prevents misunderstandings, and promotes confidence in speaking and writing.
It’s the key to expressing thoughts accurately, making a positive impression, and being understood in various contexts, from everyday conversations to professional settings.
In essence, grammar empowers you to wield the English language with precision and impact, making it an indispensable tool for effective communication and success.
Learning English Grammar is a very difficult task, especially for Non-native English speakers, they have to face many difficulties to learn English Grammar. Because, they have to start from scratch and as we know there are lots of rules, sentences, phrases, etc.
But don’t worry using proper guidance and technique as well as proper strategy you can learn English grammar and use it effectively During communication. One thing I wanna tell you is that anyone can be a master of these rules. There are various online resources and guidance available on the internet either on YouTube, Apps, or Google.
“Grammar is the basis of a language, the frame on which ideas are hung, and the loftiest imagery of thought can fall flat if ungrammatically expressed.” – J. E. METCALFE
In this blog post, you will learn the Complete Basic knowledge and Grammar course structure to Learn English. Only you need
Basics of Grammar
Understanding the basics of English grammar is crucial for English communication. So everyone must know about the basics of English grammar. In this section, we will cover basic concepts of English grammar, which include parts of his speech, grammatical sentence structure, tenses, etc.
Sentence
A group of words arranged in a definite structure, which a Complete sense is called a sentence.
Example:- We play Cricket. Kailty comes with books.
There are five types of sentences:
- Assertive Sentence
- Interrogative sentence
- Imperative sentence
- Exclamatory sentences
- Optative sentence
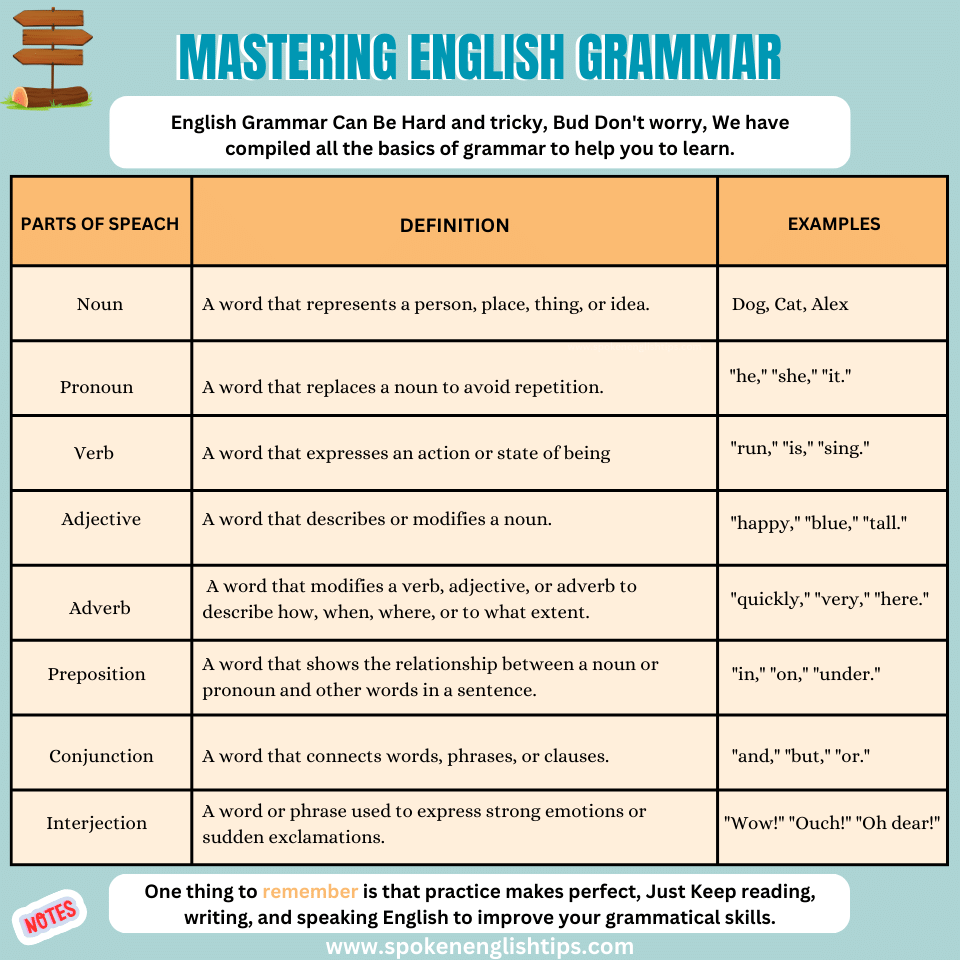
Parts of Speech
Parts of speech are the basic concepts of English grammar. Every learner must be aware of these eight parts of speech.
1. Nouns 2. Pronouns 3. Verbs 4. Adjectives 5. Adverbs 6. Prepositions 7. Conjunctions 8. Interjections.
A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. For example, in the sentence “The cat chased the ball,” “cat” and “ball” are nouns because they represent living creatures and objects.
Pronouns are words used to replace nouns to avoid repetition. In the sentence “She is going to the store,” “she” is a pronoun, replacing the need to repeat the person’s name.
Verbs are action words that express what someone or something is doing, like “run,” “jump,” or “write.” For instance, in “He runs every morning,” “runs” is the verb, conveying the action.
Adjectives modify nouns to provide more information about them. In “The blue sky,” “blue” is an adjective describing the type of sky.
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs to provide more details about how, when, or where an action occurs. In “She sings beautifully,” “beautifully” is an adverb describing how she sings.
Prepositions show relationships between nouns and other words in a sentence, indicating location, direction, time, and more. In “The book is on the table,” “on” is a preposition indicating the book’s location.
Conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses to make sentences more complex. In “I like both tea and coffee,” “and” is a conjunction connecting the two choices.
Interjections are short exclamations that express strong emotions or reactions. For example, “Wow!” and “Ouch!” are interjections conveying surprise or pain, respectively.
Sentence Structure
1. Subject and Predicate 2. Types of Sentences (Declarative, Interrogative, Imperative, Exclamatory) 3. Sentence Fragments 4. Run-on Sentences C. Punctuation 1. Periods and Commas 2. Semicolons and Colons 3. Apostrophes and Quotation Marks 4. Hyphens and Dashes
Sentence structure refers to the arrangement and organization of words and phrases to create a grammatically and syntactically correct unit of communication in written or spoken language.
It encompasses the way words are ordered to convey meaning and includes elements like subjects, predicates, clauses, and phrases.
A well-structured sentence adheres to the rules of grammar, ensuring clarity and coherence, enabling effective communication.
Different sentence structures, such as simple, compound, and complex sentences, allow writers and speakers to convey various levels of detail, emphasis, and complexity in their expressions, making sentence structure a fundamental aspect of effective communication in any language.
Tenses
Tenses in grammar are a way of indicating when an action or event takes place, helping to establish its timing and duration in relation to the present, past, or future.
They consist of four main parts:
the present tense, which describes actions happening now or habitual actions;
the past tense, which refers to actions that have already occurred;
the future tense, which pertains to actions that will happen; and the perfect tense, which denotes actions that are completed or have a connection to another point in time.
Tenses play a vital role in providing clarity and context in language, allowing speakers and writers to convey their statements effectively.
Tenses are the most important for everyone to start the conversation.
Learning the basics of English grammar is vital for clear communication. When we understand parts of speech, sentence structure, and grammar tenses, we can express ideas confidently.
Deep into English Grammar
English grammar has many rules and structures that control how we talk. To become a language expert, you need to study it deeply. In this part, we’ll look at important grammar parts like phrases, clauses, verbs, nouns, and pronouns.
Phrases and Clauses
Freedom clothes are an essential base of English grammar. A simple definition is a phrase is a group of words That functions as a single unit in a sentence. On the other hand, a Clause is a group of words that contains a subject and predicate Which can be part of the larger sentence or stand alone.
Clauses can be dependent or Independent. Independent clauses can stand as alone sentences whereas Dependent clauses can be noun clauses, adverb clauses, or adjective clauses.
Types of Verbs
A verb is a word used for saying something about some person or thing, and a verb is a word that states something about a person or a thing.
There are several types of verbs:
- Transitive Verb
- Intransitive Verb
Transitive Verb: A verb, that requires an object after it to complete its sense, is called transitive verb.
Intransitive Verb: A verb that does not require an object to complete its sense, but makes good sense by itself, is called a transitive verb.
Nouns and Pronouns
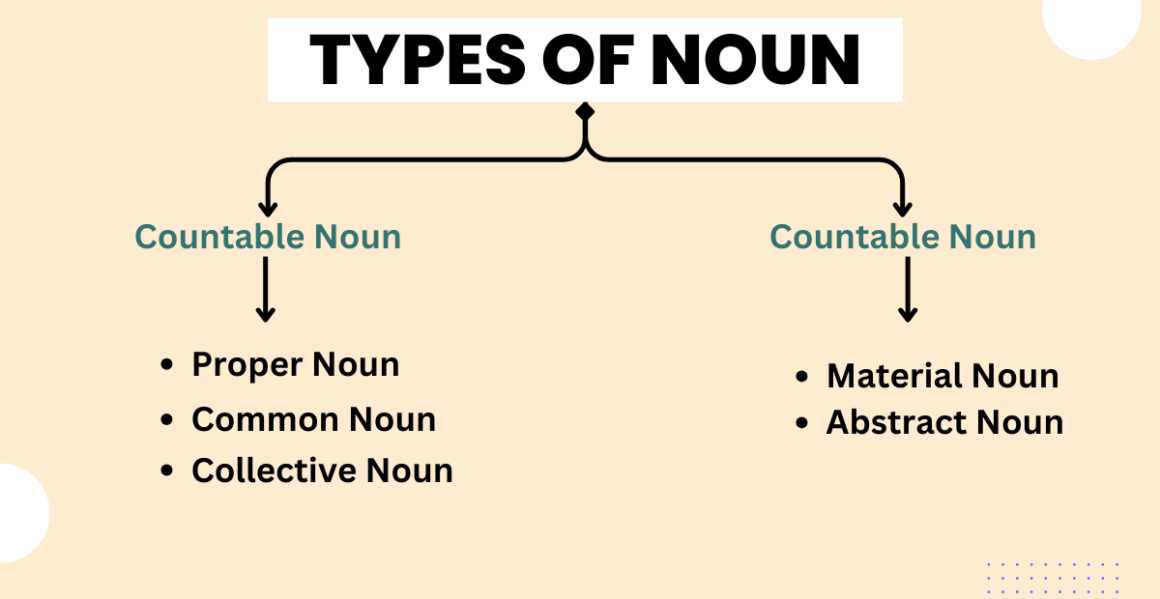
A noun is the name of a person, place, thing, quality, or thing.
Types of Nouns:
- Countable Noun
- Proper Noun
- Common Noun
- Collective Noun
- Uncountable Noun
- Material Noun
- Abstract Noun
A pronoun is a word used instead of a Noun.
Kinds of pronouns:
- Personal pronouns
- Possessive pronouns
- Demonstrative pronouns
- Distributive pronouns
- Reciprocal pronouns
- Reflexive pronouns
- Emphatic or Emphasizing Pronouns
- Indefinite pronouns
- Relative pronouns
- Interrogative pronouns
- Exclamatory Pronouns
Punctuation and Spelling
Punctuation Rules
Punctuation serves as a fundamental pillar of English grammar, playing a pivotal role in imparting significance and lucidity to the written word. Below, we outline several crucial punctuation guidelines that should be maintained:
1. Periods (.) – These bring sentences to a full stop, signaling the end of a complete thought.
2. Commas (,) – Commas are versatile; they can separate items in a list, set off introductory phrases, and create pauses for clarity within a sentence.
3. Semicolons (;) – Semicolons help connect closely related ideas within a sentence, allowing for a more extended pause than a comma but less finality than a period.
4. Colons (:) – Colons introduce lists, explanations, or quotations in a sentence, emphasizing the information that follows.
5. Question Marks (?) – These punctuate interrogative sentences, conveying a sense of inquiry.
6. Exclamation Marks (!) – Exclamation marks signify strong emotions or exclamatory sentences, adding emphasis to the content.
7. Quotation Marks (” “) – Quotation marks enclose direct speech, dialogue, or quotations from texts.
8. Apostrophes (‘) – Apostrophes denote possession or contraction in words.
9. Hyphens (-) – Hyphens connect compound words and assist in avoiding ambiguity.
10. Ellipses (…) – Ellipses indicate omitted words or a trailing-off thought in a sentence.
11. Parentheses (()) – Parentheses enclose supplementary information within a sentence, setting it apart.
12. Brackets ([] or {}) – Brackets serve to insert clarifications, corrections, or editorial comments into quoted material.
13. Dashes (—) – Dashes can emphasize or set off information within a sentence, similar to parentheses or commas.
Common Spelling Mistakes
Spelling mistakes are common errors that can occur in written communication. Here are some common spelling mistakes in grammar to avoid:
- Their/They’re/There: These homophones are often confused. “Their” shows possession, “They’re” is a contraction of “they are,” and “There” refers to a place or location.
- Your/You’re: Another set of homophones. “Your” indicates possession, while “You’re” is a contraction of “you are.”
- Its/It’s: “Its” is the possessive form, while “It’s” is a contraction of “it is” or “it has.”
- Effect/Affect: “Effect” is usually a noun, meaning the result of something, while “Affect” is typically a verb, meaning to influence or produce a change in something.
- To/Too/Two: “To” is a preposition, “Too” means also or excessively, and “Two” is the number 2.
Apostrophe
Possession: Apostrophes are used to indicate possession or ownership. For singular nouns, an apostrophe followed by an “s” is added to the noun to show possession. For example, “The cat’s tail” indicates that the tail belongs to the cat. For plural nouns ending in “s,” only an apostrophe is added after the “s,” as in “The cats’ tails.”
Contraction: Apostrophes are also used in contractions, where they replace omitted letters in a word to combine two words into one. For instance, “can’t” is a contraction of “cannot,” where the apostrophe replaces the letters “no.”
Plurals of Letters and Numbers: In some cases, apostrophes are used to form the plural of letters and numbers to avoid confusion. For example, “Mind your p’s and q’s” uses apostrophes to indicate that you should be careful with the letters “p” and “q.”
Overall proper punctuation is essential for written communication in English. By following the above rules you can reduce your mistakes in written communication.
Expanding Your Vocabulary
Vocabulary is the backbone of English speaking improvement. If you want to be a fluent English speaker or have English grammar skills just by learning new words you can enhance your communication skills.
For effective communication, you must have a good collection of words.
English Grammar
- Tenses
- What Are Tenses
- Rules Of Tenses
- Tenses Chart
- Types of Tenses
- Present Continuous Tense Exercise
- Present Indefinite Tenses Exercise
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense Exercises
- Present Perfect Tense Exercises
- Future Indefinite Tense Exercises
- Past Continuous Tense Exercises
- Past Indefinite Tense Exercises
- Present Continuous Tense
- Present Indefinite Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Indefinite Tense
- Parts Of Speech
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Simple Present Tense Examples
- Simple Past Tense Examples
- Future Continuous Tense
- Future Indefinite Tense
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense
- Future Perfect Tense
- Simple Future Tense Examples
- Parts of Speech
- Parts of Speech Examples
- Parts of Speech Exercises
- Noun
- Types Of Noun
- Common Noun
- Noun Examples
- Proper Noun
- Abstract Noun
- Collective Noun
- Concrete Noun
- Compound Noun
- Countable and Uncountable Nouns
- Material Noun
- Possessive Noun Verb
- Verb Examples
- Verb Forms
- Noun Exercises
- Noun Sentences
- Pronoun
- Types of Pronoun
- Demonstrative Pronouns
- Personal Pronouns
- Possessive Pronouns
- Pronoun Examples
- Indefinite Pronouns
- Interrogative Pronouns
- Reflexive Pronouns
- Distributive Pronouns
- Emphatic Pronouns
- Object Pronouns
- Reciprocal Pronouns
- Adverb
- Pronoun Exercises
- Pronoun Sentences
- Types of Adverb
- Adverb
- Clause
- Adverb Examples
- Adverbs of Frequency
- Adverbs of Manner
- Auxiliary Verbs
- Transitive and Intransitive verbs
- Types of Verb
- Adverb Of Place
- Adverb of Degree
- Adverb of Time
- Adverb Exercises
- Adverb Of Happy
- Adverb Sentences
- Adjective vs Adverb
- Adjective
- Linking Verbs
- Main Verb
- Non Finite Verb
- Preposition
- Preposition List
- Types Of Preposition
- Preposition Examples
- Preposition Exercises
- Preposition Rules
- Preposition Sentences
- Uses Of Preposition
- Adjective Examples
- Adjective Words
- Types of Adjectives
- Descriptive Adjectives
- Distributive Adjectives
- Interrogative Adjectives
- Adjective Phrase
- Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
- Order Of Adjectives
- Adjective Exercises
- Adjective Sentences
- Conjunction Examples
- Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Correlative Conjunctions
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Conjunction Exercises
- Conjunction Sentences
- Conjunction Worksheet
- Types Of Conjunction
- Interjection
- Interjection Examples
- Interjection Exercises
- Interjection Sentences
- Interjection Worksheet
- Types of Interjection
- Determiners
- Types of Determiners
- Determiners Worksheet
- Possessive Determiners
- Determiners Exercises
- Direct and Indirect Speech
- Direct and Indirect Speech Examples with Answers
- Direct and Indirect Speech
- Direct and Indirect Speech Rules
- Degrees Of Adjectives
- Demonstrative Adjectives
- Possessive Adjectives
- Direct and Indirect Speech Worksheet
- Idioms and Phrases
- English IdiomsIdioms and Phrases
- Idiom Examples
- Idioms List
- English Phrases
- Idioms and Proverbs
- Noun Phrases
- Phrases Examples
- Prepositional Phrase
- Adverbial Phrase
- Adjectival Phrases
- Types of Phrases
- Idioms vs Phrases
- Phrase vs Clause
- Clause Examples
- Phrases and Clauses
- What is a Clause
- Noun Clause
- Noun Clause Examples
- Adverb Clause Examples
- Relative Clause
- Relative Clause Examples
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Clause Examples
- Subordinate Clause
- Subordinate Clause Examples
- Types Of Clauses
- Conditional Clause
- Dependent Clause
- Independent Clause
- Phrases and Clauses Exercises
- Active and Passive Voice
- Active and Passive Voice Examples with Answers
- 50 Sentences of Active and Passive Voice
- Active and Passive Voice Exercises
- Active and Passive Voice Rules
- Active and Passive Voice Worksheet
- Difference Between Active and Passive Voice
- English SentenceTypes of Sentences
- Imperative Sentence
- Imperative Sentence Examples
- Assertive Sentence
- Interrogative Sentence
- Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Assertive Sentence Example
- Affirmative Sentence
- Affirmative Sentence Examples
- Exclamatory Sentence
- Exclamatory Sentence Example
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Sentence Example
- Optative Sentence
- Optative Sentence Example
- Simple Sentence
- Simple Sentence Examples
- Compound Sentence
- Compound Sentence Examples
- Complex Sentence
- Complex Sentence Examples
- Negative Sentences
- Negative Sentence Examples
- Transformation Of Sentences
- Transformation Of Sentences Exercises
- Transformation Of Sentences Examples
- Transformation Of Sentences Rules
- GerundGerund Examples
- Gerund and Participle
- Gerunds and Infinitives
- 50 Examples Of Gerunds
- Difference Between Gerund and Participle
- Participle: Definition and Examples
- Present Participle
- Present Participle Examples
- Past Participle
- Past Participle Examples
- Antonyms
- Synonyms
- Homophones
- Homophones Examples
- Homophones Words
- Homonyms
- Homonyms and Homophones
- Homophones Sentences
- Articles in English Grammar
- Modals in English Grammar
- Gender in English Grammar
- Number in English Grammar
- Degree in English Grammar
- Linkers in English Grammar
- Case In English Grammar
- Punctuation in English Grammar
- English Grammar Rules
- English Grammar Questions