Do you want to learn about the noun and its classification? here I am sharing noun complete rules and parts of a noun. learn here complete grammar rules.
What is noun and its types
a noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. It is a part of speech that is used to identify and describe the subject of a sentence.
Nouns can be singular or plural and can be further classified into common nouns, which refer to general things, and proper nouns, which refer to specific people, places, or things.
What is the Definition of noun?
A noun is a word that names a person, place, or thing. The ‘thing’ means anything which we can think like touchable, untouchable, visible, invisible, countable, uncountable, feelings, etc.
Ex- Book, table, fan, car, gold, collage, bench, queen, Rahul, rice, girl, dog, marriage, humanity, sad, etc.
A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. It is a fundamental part of speech, and it is used to name and identify people, objects, places, concepts, and more. Nouns can be singular or plural, concrete or abstract, and common or proper.
Examples of nouns include “book,” “teacher,” “city,” “happiness,” and “love.” Nouns are essential building blocks of language, and they form the basis for many other parts of speech, including verbs, adjectives, and adverbs.
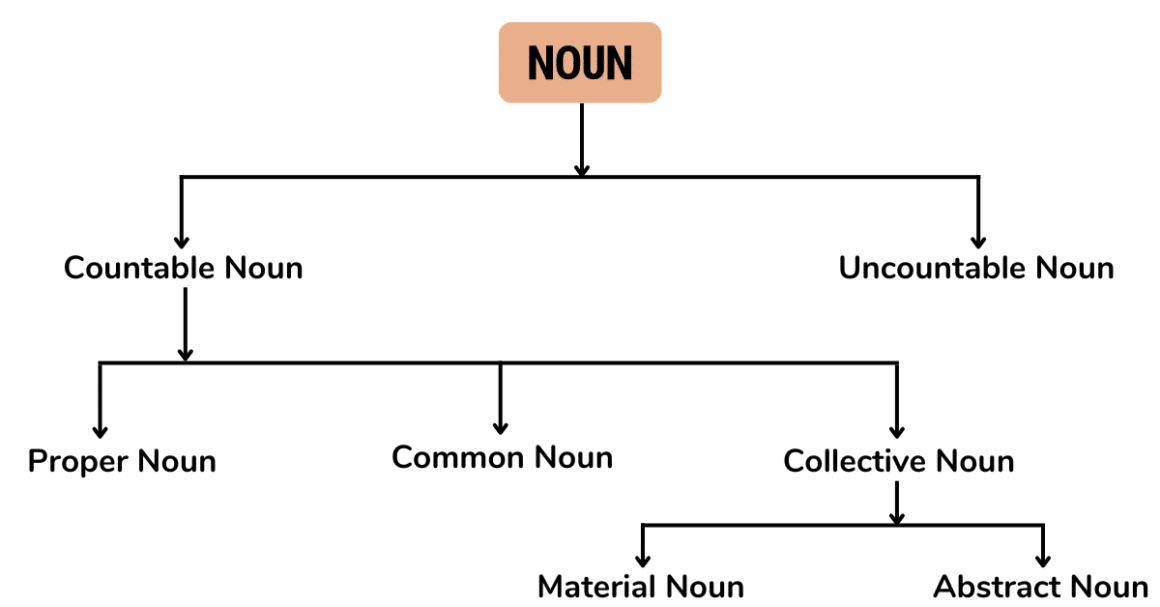
Types of Noun
There are especially six types of the noun:-
- Common noun
- Proper noun
- Collective noun
- Abstract noun
- Countable noun
- Uncountable noun
1. Common Noun: A common noun is a non-specific person, place, or thing. Common nouns are not typically capitalized. It is capitalized when it comes with the first word of the sentence.
Ex-Dog, girl, pen, chair, boy, car, etc.
2. Proper noun: A proper noun is a name given to a specific person, place, or thing. A proper noun always begins with capital letters.
Ex-India, Ram, June, Sunday, and APJ Abdul Kalam are proper nouns because each example refers to a particular person, place, or thing.
3. Collective noun: A collective noun is a noun that represents a group of persons, places, or things.
Ex- a bunch of grapes, Army, family, committee, etc.
4. Abstract noun: An abstract noun is the name of quality, action, state, taste, etc. which you cannot see, hear or taste.
Ex- happiness, sadness, honesty, laughter, youth, childhood, etc.
5. Countable noun: The countable noun which you can count is called a countable noun.
Ex- book, pen, student, doctor, cat, chair, etc.
6. Uncountable noun: Uncountable nouns are the names that you can’t count as uncountable nouns.
Coun and its Classification

Ex- Water, milk, rice, sugar, salt, etc.
Noun number – Singular and Plural
If a noun tells one and more than one is called a number.
Singular: When we talk about a single person, place, or thing is known as singular.
Ex-pen, copy, computer, chair, etc.
Plural:- When we talk about more than one person or thing is known as a plural noun.
Ex- men, computers, chairs, copies, etc.
| Singular | Plural |
| Fan | fans |
| Flat | flats |
| Shirt | shirts |
| Horse | horses |
| Pen | pens |
| Chair | chairs |
| Friend | friends |
| Dog | dogs |
| Bus | buses |
Noun and the Gender
Gender:- The noun which denotes the male or female sex is called Gender.
Ex- Cow, man, woman, horse, bitch, mother, father.
Commonly gender has been divided into four types-
- Masculine gender
- Feminine gender
- Common gender
- Neuter gender
Masculine gender:- The noun which denotes the male sex.
Ex-Boy, father, brother
Feminine gender:- The noun which denotes the female sex is known as feminine gender.
Ex-girl, mother, sister, etc.
Common gender:- The noun which does not specify the sex but only indicates a living thing is called common gender.
Ex- baby, student, professor, etc.
Neuter gender:- the noun which donates a non-living object or thing with life is called neuter gender.
Ex- tree, inkpot, pen, table, etc.
Noun and the Case
The relation in which the noun stands to some other words or the change of the form by which this relation is indicated is called the Case.
Learn Complete Spoken English
Kinds of Case
- Nominative case: A noun or pronoun that functions as the subject of a verb is placed in Nominative case.
- Objective case: A noun or pronoun that functions as an object of a verb is placed in the objective case.
- Possessive Case: When a noun shows its relation with or possession of another Noun is in the possessive case.
- Vocative case: If a noun is called, it is called the vocative case.
Do you want to improve your English fluently?
Do you want to speak like a native Speaker?
You May Also Read


