Privately issued student loans can be a good choice for students who need money for school. These loans have lower interest rates than government loans, and they usually let you pay back the money in a way that works better for you. Here are some good things about private student loans:
Since the loans don’t have a guarantee from the government, they might give you more choices on how to pay them back.
The government doesn’t promise to pay back these loans, so there’s more freedom in how you give the money back. You can use these loans for anything, not just for school fees. Usually, the interest rates on private loans are lower than the rates on loans from the government for students.
They give set prices that are less than what federal loans charge.
Usually, when you borrow money, there are two types of interest rates: fixed rates and variable rates. Fixed rates stay the same, while variable rates can change. For student loans and some other loans, fixed rates are usually lower than variable rates.
For example, federal student loans have variable rates that may go up or down, but for the 2019-20 school year, the average rate for new borrowers was 7 percent. Subsidized Stafford Loans, which are for students with low incomes, had an average rate of 5.5 percent. Private lenders, like banks, offer fixed rates that can range from 5 to 12 percent, plus additional fees.
Credit card debt usually has an average interest rate of 15%, and auto loans have an average interest rate of 4%, according to data from Bankrate collected by LendingTree in April 2019.
Because student loans are considered less risky than some other types of debt, like credit cards, private student loans are often priced lower than both federal and private loans. They are usually even lower than what you might pay with cash advances, lines of credit from your bank account, or credit cards.
Privately issued student loans offer more flexible repayment choices.
One big advantage of private student loans is that you can take more time to pay them back. Unlike government student loans, where you usually have to repay the money in 10, 15, or 20 years, private lenders let you choose to pay back the loan in a period ranging from 5 to 30 years.
This gives you more control over how much you pay each month and lets you make decisions about your career without feeling pressured.
Similar to government loans, private lenders also give you options for flexible payments. They might have plans where you start by paying a smaller amount and then gradually pay more over time.
This way, even if your salary isn’t high enough at first, you can still make progress on repaying the loan. This flexibility is helpful for people who need extra time before they start earning a full-time salary.
On the other hand, it also means you can delay paying back the loan if necessary, or in some cases, even get rid of part of the debt.
What is the advantage of private student loans over federal government loans?
| Advantage | Private Student Loans | Federal Government Loans |
|---|---|---|
| Repayment Period | Flexible terms, ranging from 5 to 30 years. | Typically fixed periods of 10, 15, or 20 years. |
| Monthly Payment Flexibility | Greater control over monthly payments. | Fixed repayment amounts, less flexible in the short term. |
| Career Choices | Allows more flexibility in career decisions. | Repayment structure may influence career choices. |
| Graduated Payment Plans | Offers graduated payment options. | May have similar options but generally more standardized. |
| Early Repayment Flexibility | Can start repaying at a slower pace initially. | Fixed repayment schedules may not be as adaptable. |
| Debt Elimination Possibility | More leeway to delay or eliminate some debt. | Limited options for debt elimination or forgiveness. |
| Applicability for Low-Income Earners | More accommodating for those with lower salaries. | May pose challenges for low-income individuals initially. |
| Overall Flexibility | Provides a wider range of repayment choices. | Offers fewer options for tailoring repayment to individual needs. |
What are the pros and cons of private student loans?
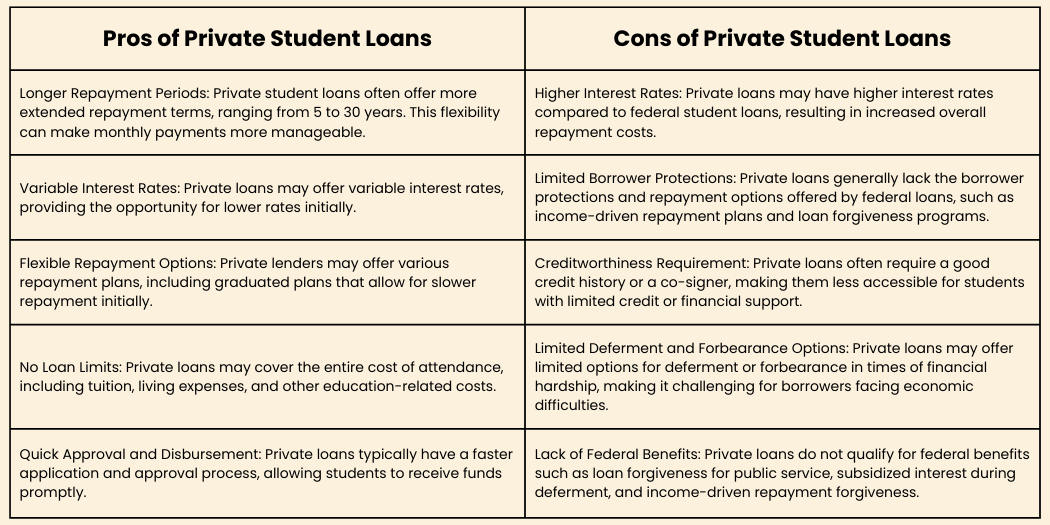
| Pros of Private Student Loans | Cons of Private Student Loans |
|---|---|
| Longer Repayment Periods: Private student loans often offer more extended repayment terms, ranging from 5 to 30 years. This flexibility can make monthly payments more manageable. | Higher Interest Rates: Private loans may have higher interest rates compared to federal student loans, resulting in increased overall repayment costs. |
| Variable Interest Rates: Private loans may offer variable interest rates, providing the opportunity for lower rates initially. | Limited Borrower Protections: Private loans generally lack the borrower protections and repayment options offered by federal loans, such as income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs. |
| Flexible Repayment Options: Private lenders may offer various repayment plans, including graduated plans that allow for slower repayment initially. | Creditworthiness Requirement: Private loans often require a good credit history or a co-signer, making them less accessible for students with limited credit or financial support. |
| No Loan Limits: Private loans may cover the entire cost of attendance, including tuition, living expenses, and other education-related costs. | Limited Deferment and Forbearance Options: Private loans may offer limited options for deferment or forbearance in times of financial hardship, making it challenging for borrowers facing economic difficulties. |
| Quick Approval and Disbursement: Private loans typically have a faster application and approval process, allowing students to receive funds promptly. | Lack of Federal Benefits: Private loans do not qualify for federal benefits such as loan forgiveness for public service, subsidized interest during deferment, and income-driven repayment forgiveness. |
